Biological Products:
Bioaugmentation products for Wastewater applications in Papermills, Refineries, Chemical, Tanneries, Municipalities, Textiles, Steel, Agriculture, Animal feedlot, Gun Powder plant, Food and Beverage- Dairy Products, Orange Juice factory, Wineries, Cookie factory, Vegetable processing plant, Meat packing, Barbecue Restaurant, Aquaculture, Ornamental Ponds with algae , CAFO, Nursing homes, Military, Campgrounds, Universities, Regulatory agencies, River and Lake remediation
Lab Services:
Filamentous Identification Lab Service. One reason to identify filaments is to determine the filaments characteristics and then determine the type present. If the type is found out, a root cause can usually be associated with a particular filament. If the cause is known, then a correction can be made to alleviate problems. Chlorination is only a quick fix. Without process changes, filaments will grow back after chlorination. Wastewater Biomass Analyses and Cooling Tower Analyses also available
Training Materials:
Training is an integral part of any job. Not everyone is at the same level of training. Many people want beginning concepts and basics. Some need technical information or troubleshooting. Some want equipment, technology or process information. We have developed a full set of Basic training, Advanced training, Filamentous Identification the Easy Way as well as custom training CD's Manuals. We also provide hands-on training classes and soon will have an Online "E-University".
Audits and Consulting:
At Environmental Leverage® Inc., we have a team of experienced individuals who come into your plant with a fresh pair of eyes. The system is checked from influent to effluent. System optimization, equipment efficiency and operational excellence are key components explored. Key Benefits Equipment efficiency Total Cost of Operation reductions Reliability and safety An onsite audit is conducted to examine system parameters, process controls, and current monitor and control procedures. A physical walk-through is conducted, process flow diagrams are examined, previous design criteria are examined and current standard operating procedures are evaluated along with data logs.
|
Free Swimming Ciliates
What's New!
We now have a brand new "Higher Life Form videos" in our Training CD list. Check out our new Wastewater Training Materials. We are also in the process of developing new courses for our ""Online University" in order to meet the needs of our global customers that cannot travel to our public classes. WastewaterElearning.com/Elearning
We hope you like the new look of our Higher Life form Identification Pages
If you would like more information on bacteria, filaments or higher life forms, you might want to consider purchasing our Wastewater Microbiology Training materials. We also have our lab that can perform a Wastewater Biomass lab analyses of your own MLSS for more information
Free Swimming ciliates
Identification The Ciliates are more complex organisms than the amoebae and flagellates. Over 7000 known species exist of some of the most complex single-celled organisms ever. Free swimming ciliates are covered with cilia, hair-like projections, which are uniform and aligned in rows. The ciliates move and capture food by means of the cilia. The anterior portion of the ciliate is the oral region which is also covered with cilia. Free swimming ciliates range in size from 20-400 µm and have two kinds of nuclei. Sexual reproduction is by conjugation. Free-swimmers swim faster than flagellates so they can out compete them for food. Ciliates feed on bacteria not on dissolved organics. While bacteria and flagellates compete for dissolved organics, ciliates compete with other ciliates and rotifers for bacteria. They are usually an indicator of good quality sludge. They are typically found in young to medium age sludge.
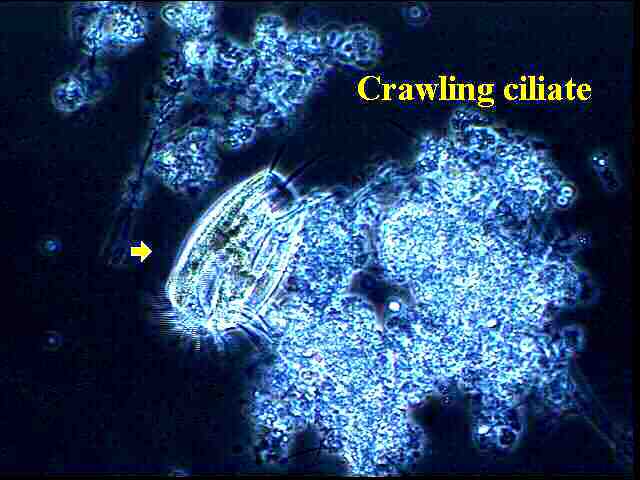
Crawling ciliates, similar to free swimming ciliates are covered with cilia, hair-like projections, which are uniform and aligned in rows. The ciliates move and capture food by means of the hardened cilia. The anterior portion of the ciliate is the oral region which is also covered with cilia. Crawling ciliates range in size from 20-400 µm.
Additional Information: Free swimming ciliates are protozoa that are in the phylum Ciliophora. Many different types of free swimming ciliates exist, including "crawling" ciliates`. Some types commonly found in wastewater are Paramecium, Euplotes, and Aspidisca.
Hypotrichs (Crawling ciliates) Crawling ciliates have cilia mainly on the lower surface of their bodies that make them appear to be legs. These are organisms with compound ciliary organelles called cirri used to walk on. They are usually dorso-ventrally flattened. Common types found in wastewater are the Genus:Aspidisca and Genus:Euplotes In order for crawling ciliates to be dominant, there must be large floc structures present that impede the free-swimmers and flagellates movement and provide a surface for the crawlers to "walk" on. This means the F:M is getting lower and the bacteria have started to formulate floc structures. Crawlers also require a high D.O. content in the mixed liquor. Sludge age is closer to middle ages than young. Crawling ciliates usually indicate a stable wastewater environment and a healthy sludge.
Environment They are found in various types of water, including freshwater and wastewater. Free swimming and Crawling ciliates are important because they work with the bacteria. They feed on the bacteria and thus help to clarify the effluent. These can be found during most sludge ages but are dominant during the middle sludge ages in your wastewater treatment plant.
If the biomass is really old and rotifers and nematodes are usually present, and all of a sudden large numbers of free swimming ciliates show up, check to see if a sudden spike of BOD has occurred. Adjustments to RAS and wasting may need to be made in order to handle the sudden increase in BOD. Addition of biological products can also help overcome sudden spikes in BOD to help recover quicker and reduce changes or BOD or TSS permit violations.
How to find them: Microscopic examination of a wet mount. Some of the larger amoebae can be seen at 40-100x and 200x.
It depends upon what the rest of the biomass looks like. If the
floc is small, weak, dispersed, you may have a young to medium age sludge.
Typically the presence of free swimming ciliates indicates a medium loading
of food vs. the amount of biomass available to eat the organics. Free
swimming ciliates indicate a relatively healthy system, no toxicity,
progressing along in a sludge age. If mixed in with the right amount of
stalked ciliates and a rotifer or two, you are probably doing very well in
your wastewater treatment system.
What should I do if there is a
significant change in my higher life forms and all of a sudden there is an
increase in free swimming ciliates?
You might want to adjust your wasting or RAS levels. Some plants add
bioaugmentation products in cases of higher loadings. You might need to
slightly increase the dosage of product. If using micronutrients, adjust
these levels also if the loading is significant.
More to come soon! For more information on Higher Life Form Identification More photos to come. . .
If you need more information on our Filamentous Identification the Easy Way Training CD or on Internet training on Filamentous bacteria, causes and controls. How and why on Wastewater Biomass Analyses
|

 When
trying to determine species in a biological wastewater treatment plant, stick to the basics, and focus on the causes
and controls of the higher life forms present. The main point of any
wastewater biomass identification is not
to get a PhD, but to fix your wastewater plant!
When
trying to determine species in a biological wastewater treatment plant, stick to the basics, and focus on the causes
and controls of the higher life forms present. The main point of any
wastewater biomass identification is not
to get a PhD, but to fix your wastewater plant!
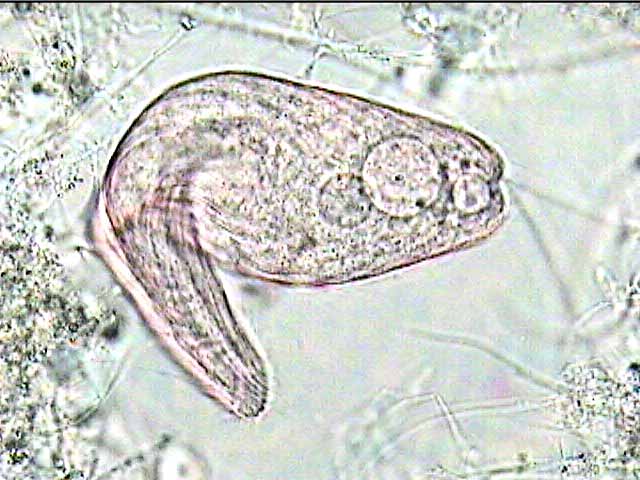 What
does it mean when I see an increase in Free Swimming Ciliates in my system?
What
does it mean when I see an increase in Free Swimming Ciliates in my system?